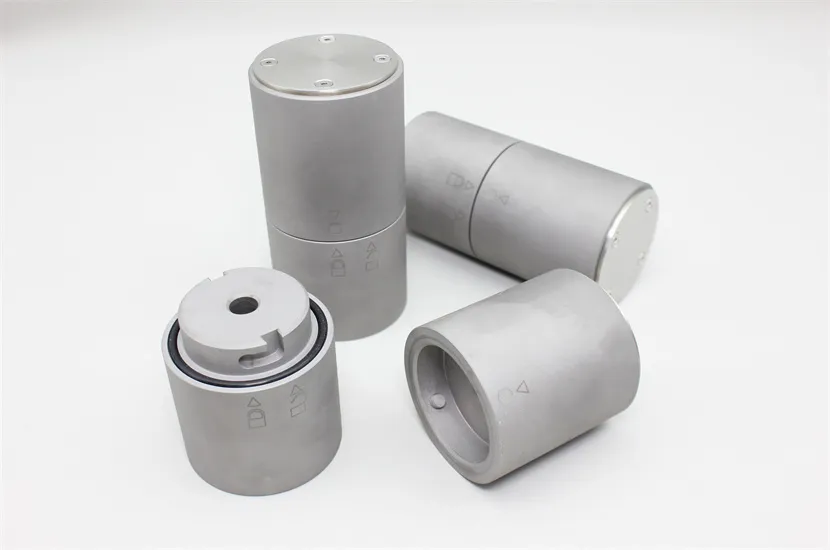
Tungsten Heavy Alloy (WHA) Shielding – The Superior Radiation Protection Solution
| Payment Type: | T/T |
| Incoterm: | CIF,FOB,Express Delivery,EXW,FCA |
| Min. Order: | 5pcs |
| Transportation: | Ocean,Air,Express |
Attributes
Model No.: JDTG-CM-063
Brand: ZZJD
Place Of Origin: China
Size: Custom-made
Material: 95% Tungsten
Denstiy: 18.1g/cm3
Surface: Polished
PACKAGING & DELIVERY
Selling Units : PCS
Package Type : Standard export packing
DESCRIPTION
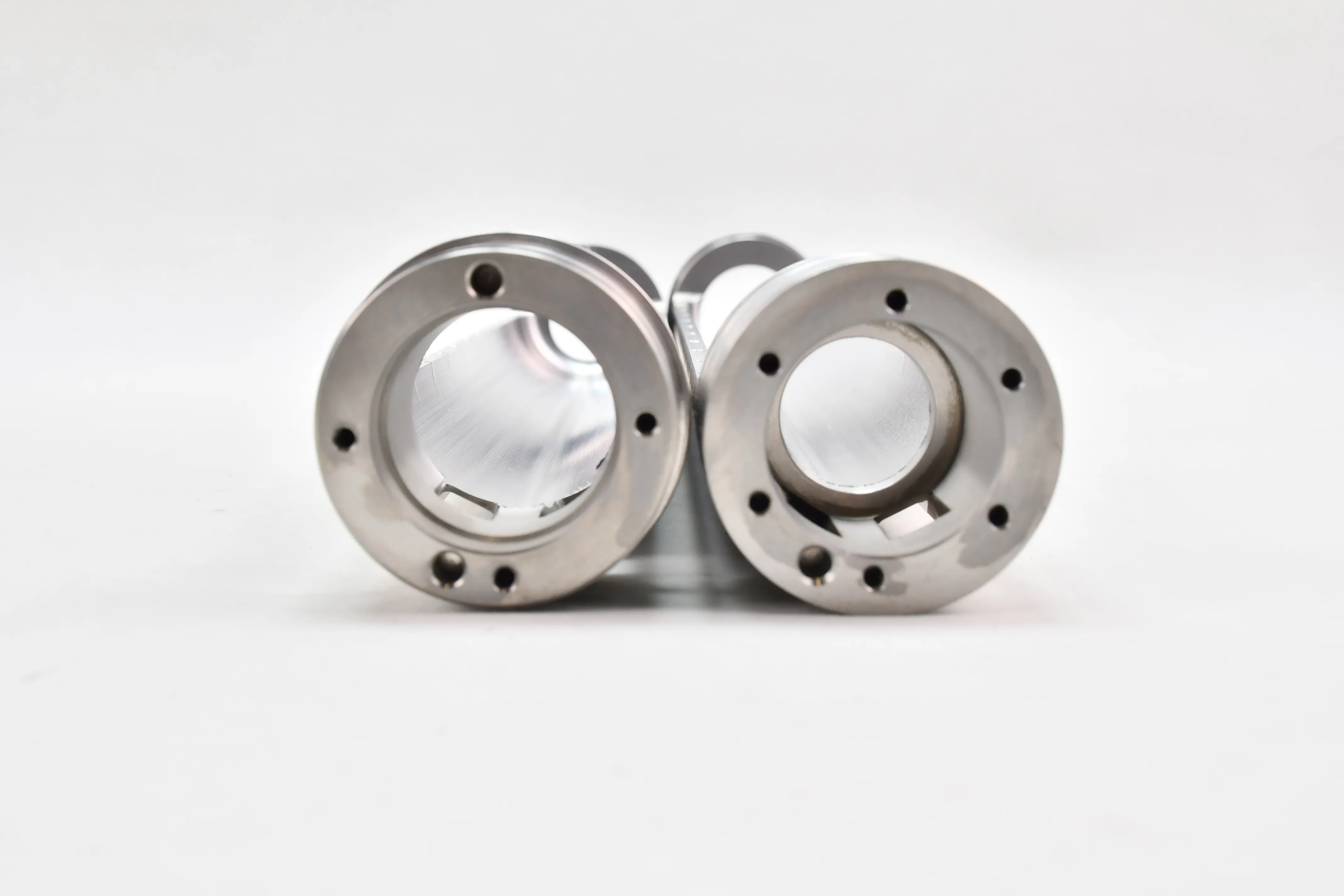
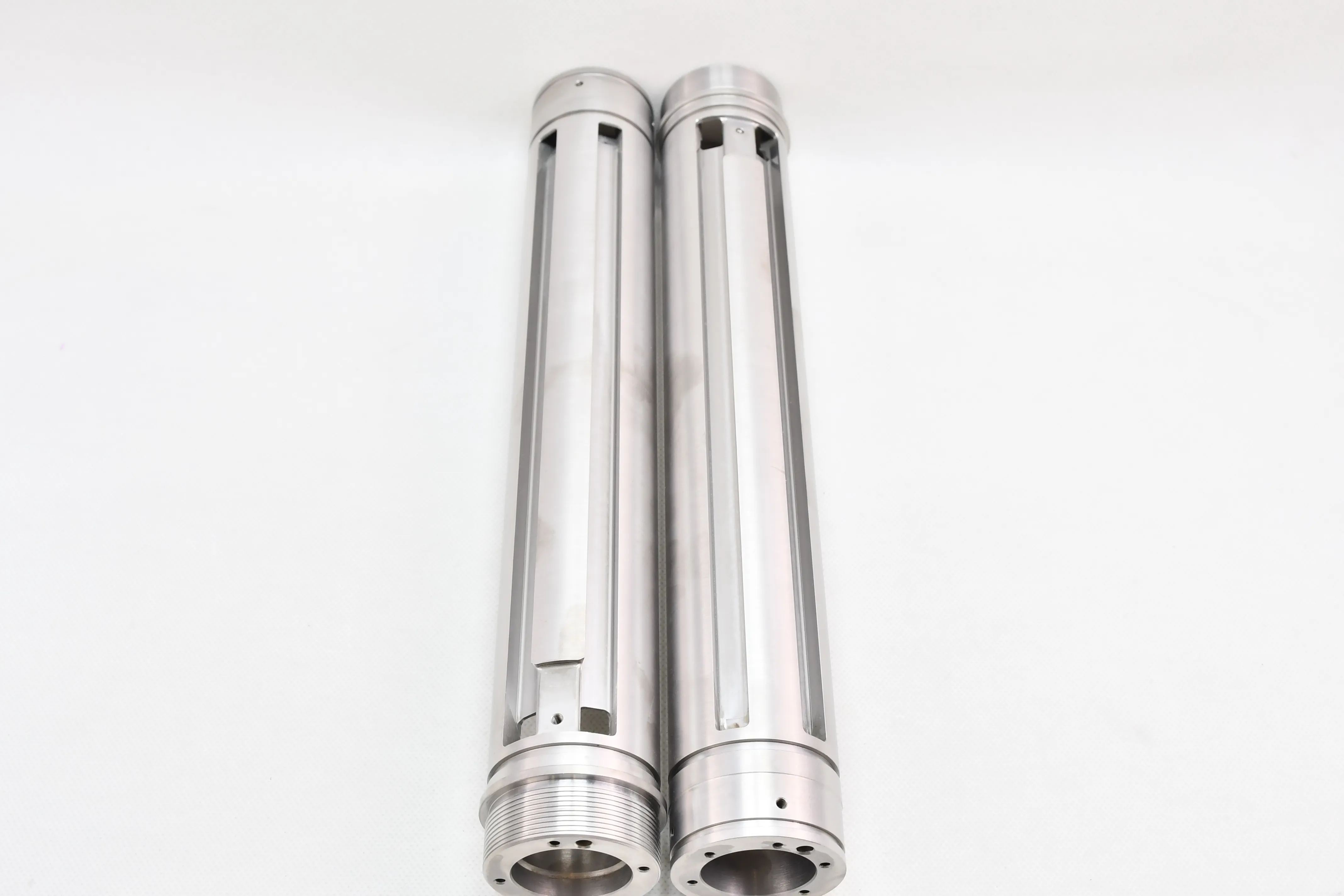
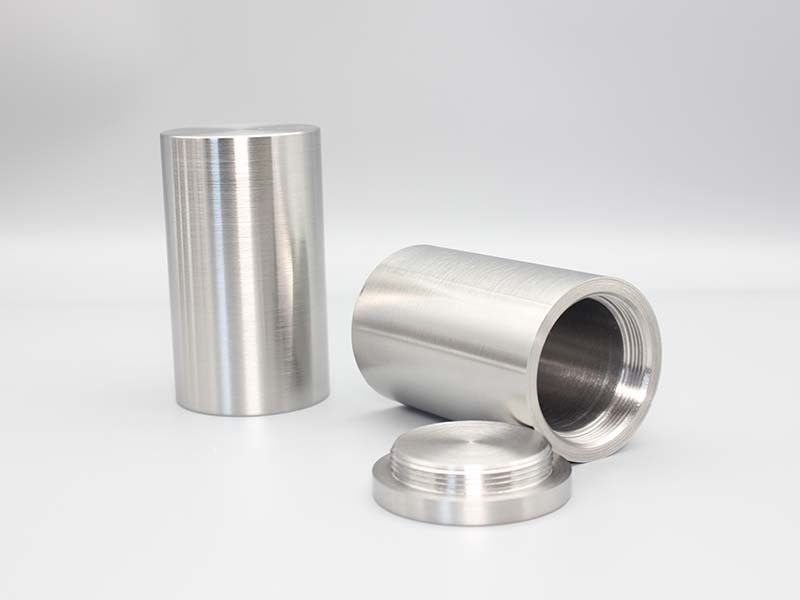
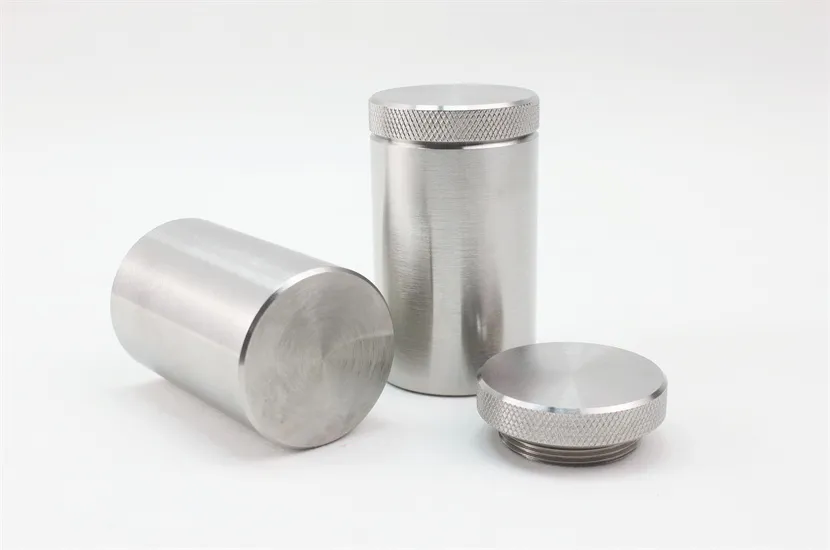
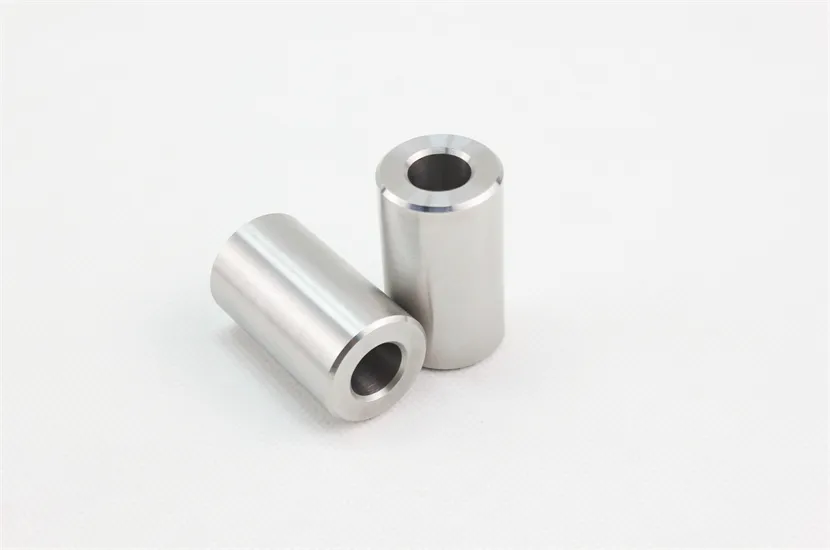
Tungsten heavy alloy shielding is a high-efficiency radiation protection component made from tungsten heavy alloys (mainly WNiFe or WNiCu systems, with tungsten content 90–97% and density 15.8–18.75 g/cm³). It is a mainstream environmentally friendly alternative to traditional lead shielding, widely used in nuclear, medical, industrial, and aerospace fields to block X-rays, gamma rays, and neutron radiation.
Key Performance Characteristics
Superior Radiation Attenuation Efficiency
Tungsten has a high atomic number (Z=74), which can effectively absorb high-energy photons through photoelectric effect, Compton scattering, and pair production. For the same shielding effect, the thickness of tungsten heavy alloy is only 1/2–2/3 of lead—this compactness is critical for miniaturizing shielding devices.
For neutron radiation, doping the alloy with boron (B) or gadolinium (Gd) can enhance neutron capture ability, expanding its application in nuclear reactor shielding.
Environmental Friendliness & Safety
Unlike lead, tungsten heavy alloys are non-toxic and do not produce harmful heavy metal pollution during production, use, or disposal. They comply with strict environmental regulations (e.g., RoHS, REACH) and avoid occupational health risks caused by lead exposure.
Excellent Mechanical & Dimensional Stability
Tungsten heavy alloys have high tensile strength (900–1100 MPa) and hardness (HB 280–350), and can be processed into complex shapes (curved plates, special-shaped blocks, hollow cylinders) without deformation. They maintain structural integrity under vibration, impact, or temperature cycling conditions, unlike soft lead which is prone to damage.
Good Corrosion Resistance
The alloy is resistant to humid, saline, and mild acid-alkali environments. Surface treatments such as nickel plating or epoxy coating can further improve corrosion resistance for long-term use in harsh industrial settings.
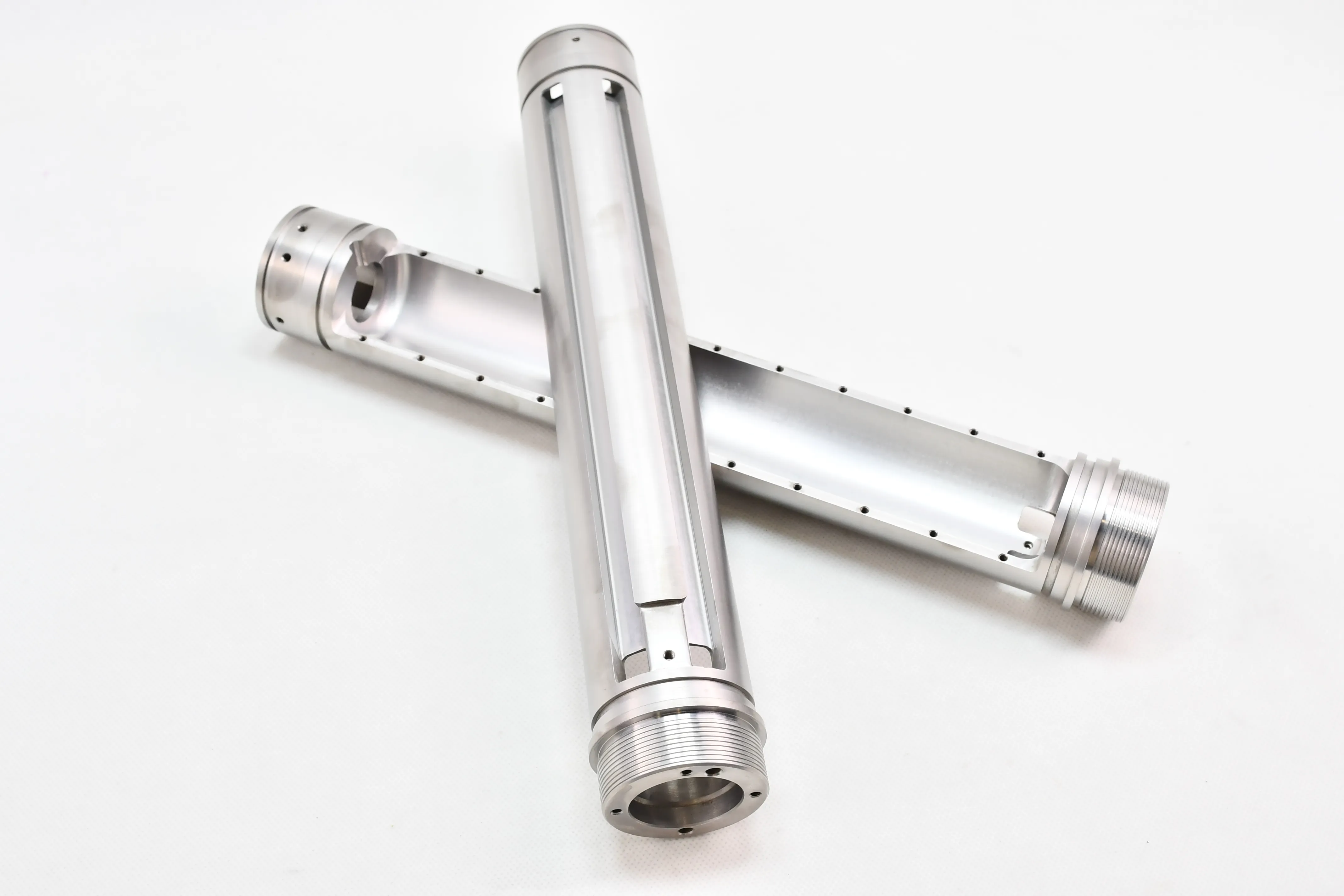

Shielding Mechanisms
Photoelectric Effect – Dominant at lower energies (<500 keV)
Compton Scattering – Primary mechanism for mid-range energies
Pair Production – Becomes significant above 1.022 MeV
Production Process
Tungsten heavy alloy shielding is manufactured via powder metallurgy technology, which ensures uniform density and radiation shielding performance:
Powder Preparation: Mix tungsten powder with nickel/iron/copper binder powder (and neutron-absorbing elements like boron if needed) by wet mixing to ensure homogeneity.
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP): Press the mixed powder into a shield blank under high pressure (200–300 MPa) to form a dense preform.
Sintering: Sinter the blank in a hydrogen atmosphere at 1400–1600°C to form a fully dense tungsten heavy alloy billet with a density of over 98%.
Precision Machining: Use CNC milling, grinding, or wire cutting to process the billet into shielding components with precise dimensions, including mounting holes, grooves, or curved surfaces.
Surface Treatment: Apply plating, painting, or passivation to enhance corrosion resistance and surface finish.
Application Fields
Medical Industry
Radiotherapy Equipment: Shielding for linear accelerators, cobalt-60 therapy machines, and proton therapy systems to prevent radiation leakage and protect medical staff and patients.
Diagnostic Equipment: Shielding blocks for CT scanners, X-ray machines, and PET-CT detectors to reduce background radiation interference and improve imaging quality.
Radioactive Drug Handling: Containers and syringes for storing/transporting radioactive isotopes (e.g., iodine-131) in nuclear medicine departments.
Nuclear Industry
Nuclear Power Plants: Shielding for reactor cores, spent fuel storage pools, and nuclear waste transport containers to block gamma and neutron radiation.
Nuclear Research: Shielding for particle accelerators, nuclear physics experiment devices, and radioactive material laboratories.
Industrial Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Shielding for industrial X-ray and gamma ray flaw detectors, used to inspect the internal structure of aircraft components, pipeline welds, and pressure vessels—protecting operators from radiation exposure.
Aerospace & Defense
Spacecraft Shielding: Radiation protection for satellite nuclear power systems and astronaut cabins to resist cosmic ray and solar flare radiation.
Military Equipment: Shielding for portable radiation detectors, nuclear weapon components, and armored vehicle radiation protection systems.

 EN
EN AR
AR FR
FR DE
DE HI
HI IT
IT JA
JA KO
KO PT
PT RU
RU ES
ES ID
ID LV
LV VI
VI HU
HU MS
MS GA
GA BE
BE YI
YI EU
EU






